Alongside such terms as crypto, blockchain technology, and the metaverse, Web 3.0 is one of the biggest buzzwords of our time. Behind it lies the idea of a whole new internet that is supposed to bring about a real revolution.
But what is Web 3.0, and what does it actually do? How far is reality from the idea? And can it be implemented at all? Let’s take a look at the most pressing questions concerning modern web technologies and digital assets.
Hi there! I’m Zifa, a passionate crypto enthusiast who’s been diving deep into the world of cryptocurrency through my writings for the past three years. My primary interest lies in exploring the profound influence of technology on society. Excited to share my insights with you all!
Definition: What Is Web3 (or Web 3.0)?
Web 3.0, colloquially known as “The Semantic Web,” represents the next evolutionary phase of the internet. It’s not merely an upgrade in design or functionality but a profound transformation in how users interact with, comprehend, and generate content online. This new era aims to foster a more intelligent, decentralized, and user-centric web, breaking away from the centralized paradigms of the current internet. This shift is often referred to as the paradigm shift towards a decentralized internet.
Key Features of Web 3.0:
- Ubiquity: Web 3.0 envisions a universal online experience across diverse devices and platforms. Whether accessed via a smartphone, a computer, or a wearable device, the user experience will be adaptive, consistent, and tailored to individual preferences. The integration of mobile phones will ensure that Web 3.0 is accessible to everyone, everywhere.
- Semantic Web: At the heart of Web 3.0 lies the Semantic Web, which goes beyond mere text and images. It understands the context of content, paving the way for enhanced search results, more pertinent content suggestions, and a more intuitive user journey. This understanding is powered by semantic metadata, which provides context to the content.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will be deeply woven into the fabric of Web 3.0. From intelligent chatbots to sophisticated recommendation engines, artificial intelligence will shape user experiences, making them more interactive and personalized.
- Spatial Web and 3D Graphics: The future of the web is immersive. With advancements in AR and VR, websites and applications will transition from flat interfaces to engaging three-dimensional spaces, offering an immersive experience to users.
- Decentralization and Blockchain: Perhaps the most groundbreaking feature of Web 3.0 is its shift towards decentralization. Blockchain technology will be the cornerstone of this movement, ensuring data transparency, security, and independence from centralized entities. This shift away from a central authority is what makes the decentralized internet so revolutionary.
How Will Web 3.0 Work?
In the eras of Web 1.0 (often referred to as the static web or read-only web) and 2.0, HTML was the primary tool for defining web page layout and content delivery. While it remains crucial in Web 3.0, the way it interacts with data sources, as well as the nature of these sources, will undergo significant changes.
Web 2.0 largely depended on centralized databases to provide data and facilitate application functions. In contrast, Web 3.0 will harness decentralized blockchains devoid of any central governing body. This democratized approach promises users greater autonomy over their online interactions and data usage. Decentralized data storage will redefine how we store data, ensuring that it’s not controlled by a single entity.
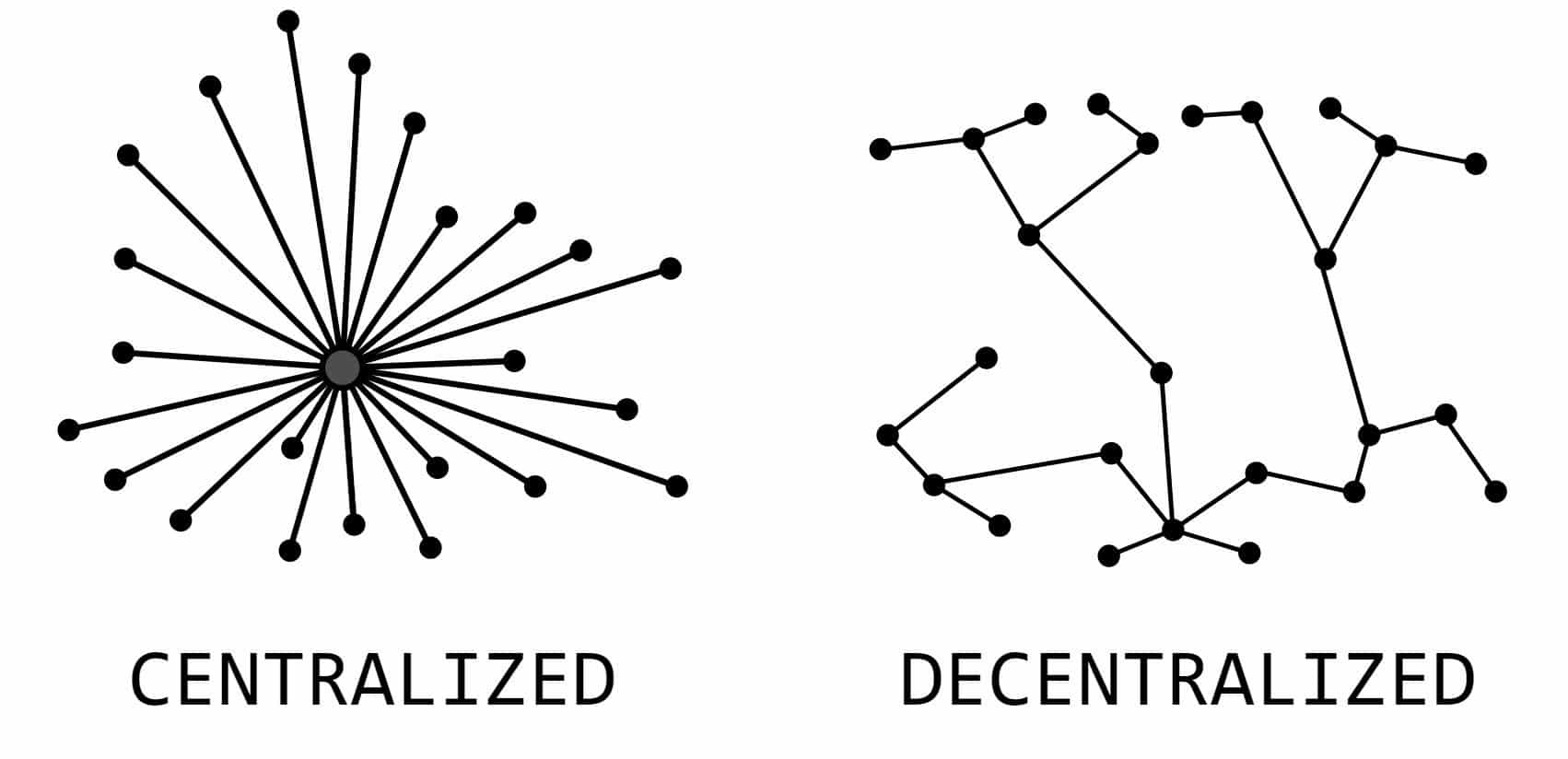
One of the stark differences between Web 2.0 and 3.0 is the role of AI and machine learning in content delivery. While Web 2.0 primarily allowed users to contribute to site content, Web 3.0 will leverage the Semantic Web and AI to automate this process, making the web more “intelligent” and responsive.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) could redefine web governance by transferring control from centralized entities to self-regulating digital communities. Furthermore, with Web 3.0’s inherent reliance on cryptocurrency, financial transactions will transition from traditional financial institutions to decentralized finance platforms on blockchains.
Considering the exponential growth of the web, Web 3.0 will require a vast number of internet addresses, which IPv6 is poised to provide, moving beyond the limitations of IPv4 used in Web 1.0 and 2.0.
Key Applications of Web 3.0
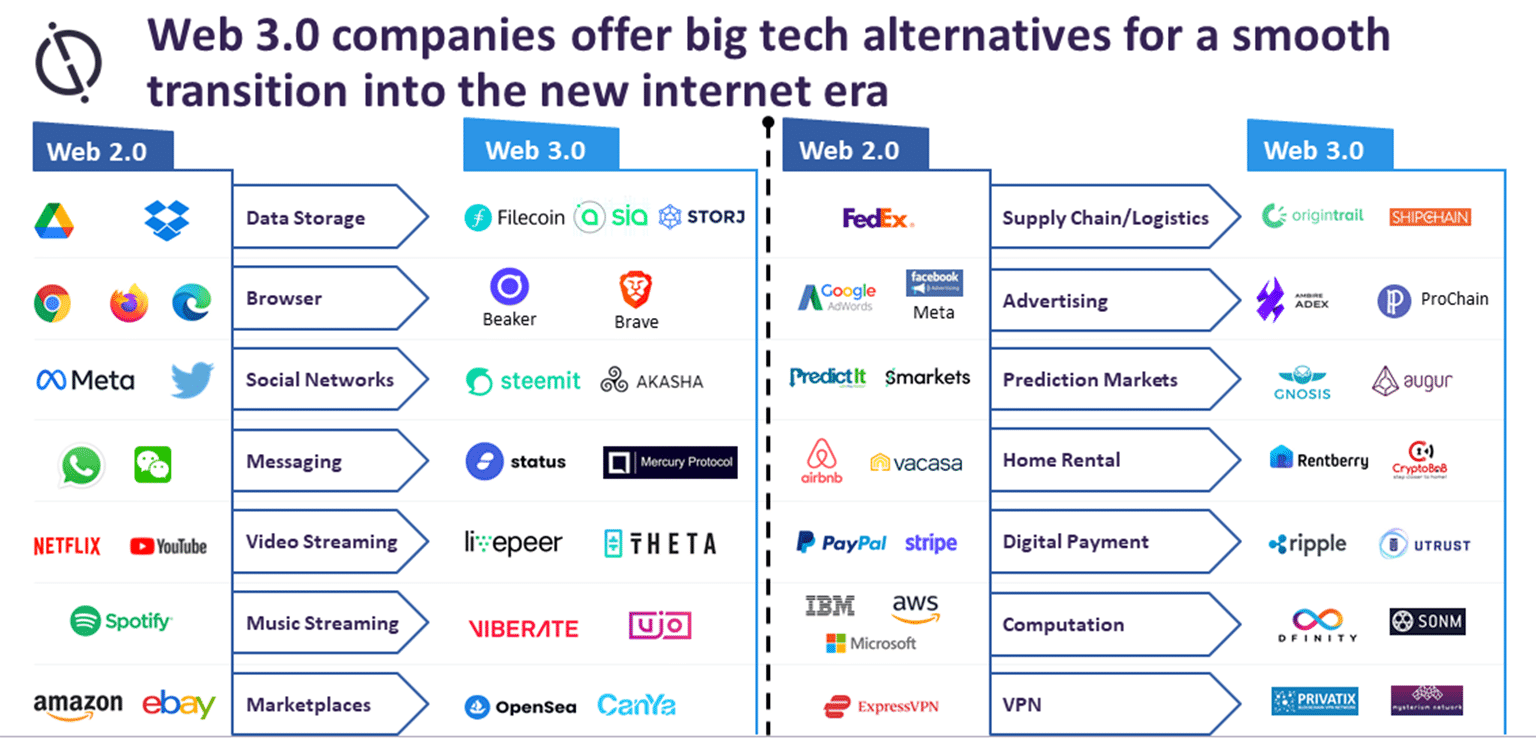
- Metaverse: The metaverse, a virtual realm, can be visualized as a 3D internet, a digital reflection of the real world. Users can navigate this space using computers, phones, or VR/AR headsets. While tech giants like Meta (formerly Facebook) and Google have heavily invested in its development, Web 3.0 offers a decentralized vision of the metaverse, emphasizing open-source, interoperability, and fair rewards for creators. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) will play a significant role in this space, representing unique digital assets.
- Blockchain Gaming: Following the success of games like Axie Infinity, the play-to-earn model became a sensation. Despite the challenges, the fusion of gaming and decentralized technologies promises a resurgence, especially when the focus shifts to enhancing player experience.
- Creator Economy: Web 3.0 empowers creators by allowing them to directly connect with their audience, bypassing intermediaries like YouTube or Spotify and ensuring a fairer revenue distribution.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): DAOs represent a potential future organizational structure, leveraging smart contracts to create self-governing entities that transcend geographical boundaries.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Decentralized finance (DeFi) exploded in value in mid-2020, having enabled cryptocurrency users to invest, borrow, lend, trade, and stake crypto assets permissionlessly. While DeFi faced its fair share of security issues like hacks and scams, the industry offers Web 3.0 the opportunity to onboard potentially billions of users neglected by traditional finance firms such as banks.
What Is the Difference Between Web 3.0 and Metaverse?
Despite frequent synonymous usage, “Web 3.0” and “Metaverse” are distinct concepts. Web 3.0 describes the next internet iteration, emphasizing decentralization and user empowerment, safeguarding against undue censorship and data misuse. In contrast, the metaverse refers to interconnected virtual worlds where users’ digital avatars interact through various activities, such as owning unique digital assets (e.g., virtual land or items).
Since Virtual Reality (VR) offers an immersive experience mirroring real life, it is pivotal for a successful metaverse. However, Web 3.0 doesn’t inherently require VR. Currently, most metaverse projects operate on PCs or mobile devices, but many will integrate Web 3.0 technologies for scalability in the future.
Even though a metaverse can function without decentralized technology, as showcased by Meta, a global-scale metaverse will likely necessitate Web 3.0 services, such as graphics processing and data storage. Consequently, Web 3.0 is poised to become an essential component of all metaverses, further popularized by the integration of crypto assets.
What Is Web 2.0?

As we navigate our online lives in the 21st century, we find ourselves entrenched in the Web 2.0 phase. This era is primarily characterized by co-creation and the democratization of content creation. A significant catalyst for this evolution was social media, which democratized the digital landscape, ensuring that anyone could create, upload, and redistribute content. This shift is why it’s often dubbed the “social web.”
This participatory approach marked a transformative departure from the earlier days of the internet. In Web 1.0, users were mostly passive consumers of content, with tech companies holding the reins. However, with Web 2.0, the current generation of users embraced a more active role, no longer bound by the constraints of a single company’s platform. This active engagement in intelligent creation and direct ownership of content is set to be amplified even further in Web 3.0.
Web 3.0 Benefits
The great advantage of Web 3.0 would, of course, be the immense amount of freedom that each individual user would have. Many processes would no longer be tied to large companies, instead taking place via alternative platforms and decentralized data networks.
Another goal of Web 3.0 is to democratize the internet, i.e., to create equal rights for everyone and to make it possible to make decisions on the basis of majority and consensus. Basically, on a decentralized web, every user would be able to help shape the internet (provided they have the necessary technical skills).
Here are some other benefits that Web 3.0 has:
- Every person on the network automatically has permission to use the service. Explicit permission is no longer required.
- No centralized management in applications — therefore, less censorship and more freedom in user contributions.
- Direct payments.
- Universally programmable.
- Increased — and more decentralized — user interaction.
- Great for monetizing online presence, both for application operators and for users themselves.
To put it simply, this means that there would be no censorship of any kind, neither of the content nor internet users. Moreover, no personal data will be required for payments on Web 3.0, which will promote DeFi — decentralized finance. Web 3.0 servers will be protected from being filled in by the decentralized network that continues to run in the background.
Web 3.0 thus promises not only freedom but also greater security at the same time — at least in theory. Those who don’t give out data when making payments also minimize the risk of data theft.
Web 3.0 Risks
Of course, besides opportunities, Web 3.0 also harbors dangers. For example, it will be more difficult to ensure a transparent and secure environment.
That’s because even if the promise of absolute freedom sounds tempting at first sight, there are some areas where not much can be done — for example, law enforcement.
Ensuring a certain level of security for individuals on this revolutionized internet is becoming a more challenging task, especially in terms of harassment, bullying, and fraud. What could previously be taken over, at least in part, by companies would suddenly become the responsibility of each individual.
The hype surrounding “the new internet” also harbors a certain risk because the sudden upswing in the topic could be a bubble that threatens to burst soon.
Although there is much investment in the idea of the Semantic Web, some of the necessary technologies and infrastructures are yet to be created. Therefore, Web 3.0 is still far from being ready for the mass market.
When Is Web 3.0 Coming?
At present, it is not yet possible to predict when we will find ourselves completely in the Web 3.0 stage. Even though there is a talk in some places on the World Wide Web that we already have one foot set in Web 3.0, the public is clearly not ready for it — at least, not yet.
One of the reasons for this is that many key structures are currently firmly in the hands of companies, such as Google, Microsoft, or Amazon. However, if these corporations decide to move in the direction of Web 3.0 — as Meta has done before — it could certainly be reached faster.
However, users must also embrace this change and play an active role in shaping it. After all, they are the ones who will play the most crucial role in the “new internet,” the future web. Unfortunately, it seems like we are not at that point yet. It will definitely take at least a few years until we can say we have fully arrived at Web 3.0.
Web 3.0: FAQ
Is Web 3.0 the future?
Most definitely, Web 3.0 is poised to be the future of the internet. It represents a transformative shift towards a more decentralized, user-centric, and secure online ecosystem. With its emphasis on user empowerment, data privacy, and decentralized applications, Web 3.0 offers a vision of the internet that is more in line with the original ideals of a free and open web.
Who started Web 3.0?
The term “Web 3.0” was coined by Gavin Wood in 2014, laying the foundation for a new era of the internet. However, it’s essential to acknowledge Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. While Wood introduced the concept of Web 3.0, Berners-Lee’s vision and principles have always leaned towards a more decentralized and user-centric internet, which aligns with the ideals of Web 3.0.
Does Web 3.0 exist yet?
Web 3.0 is currently in its nascent stages. Many of the foundational technologies and principles have been defined, but we are still in the early phases of its development and adoption. As with any technological evolution, it will take time for Web 3.0 to fully mature and become the dominant form of the internet.
How to make money in Web 3.0?
One of the primary avenues to explore in Web 3.0 for financial opportunities is investing in crypto projects. As the decentralized web grows, numerous projects are emerging with promising potential. For those interested in diving deeper into this realm, we have an article titled “Best Crypto to Buy Now” that provides insights and recommendations.
What is Web 4.0?
As of now, Web 4.0 is a speculative concept and hasn’t been clearly defined. Web 3.0 focuses on decentralization and user empowerment; any discussion about Web4 is purely theoretical. It’s anticipated that Web 4.0, if it emerges, would build upon the foundations of Web 3.0, possibly integrating more advanced technologies and concepts that we haven’t fully grasped yet.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.



