Funds collected by ransomware assaults fell to $456.8 million in 2022 from a excessive of $765.6 million in 2021, in line with a brand new report from analytics agency Chainalysis.
Crypto-related ransomware assaults have seen a steep fall in success fee over the past 12 months.
Crypto ransomware exercise
The chart beneath reveals the rise and fall of funds acquired by ransomware assaults over the previous 6 years. A dramatic enhance was seen in 2020 as stolen funds hit $765 million, with 2021 seeing comparable quantities stolen by unhealthy actors.
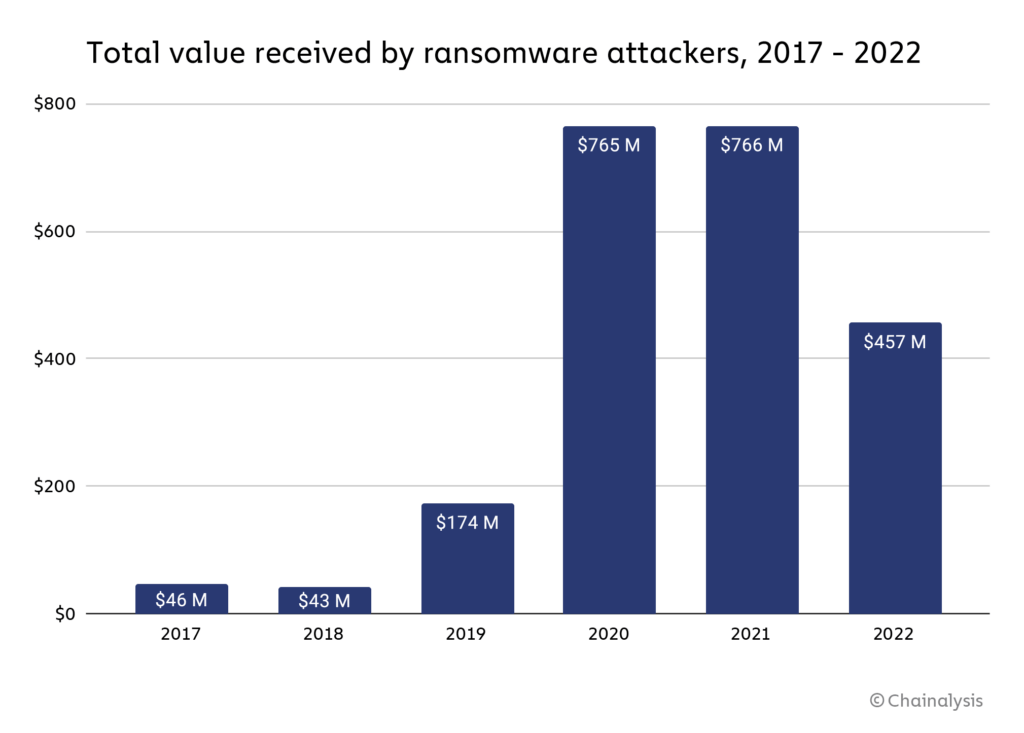
Whereas the Chainalysis report acknowledged that “the true totals are a lot greater” as it’s doubtless that there are addresses owned by ransomware attackers that haven’t but been recognized, the autumn signifies victims have gotten sensible to such assaults. Consequently, Chainalysis made a press release supporting this sentiment.
“[Ransomware payments falling] doesn’t imply assaults are down… We imagine that a lot of the decline is because of sufferer organizations more and more refusing to pay ransomware attackers.”
Ransomware Strains explode
Though funds to take away ransomware have fallen dramatically, the variety of ransomware strains exploded in 2022. A pressure is a kind of ransomware with frequent variants: Royal, Ragnar, Quantum, Play, Hive, and Lockbit.
Fortinet, a number one cybersecurity {hardware} and software program firm, reported over 10,000 distinctive strains lively all through 2022.
Strains have a lowering lifespan as unhealthy actors proceed to differ assault vectors to optimize the quantity of stolen funds. For instance, in 2012, strains lasted 3,907 days, whereas in 2022, the typical size was simply 70 days. Consequently, cybersecurity options should sustain with an growing variety of lively strains of their protection technique.
Ransomware funds
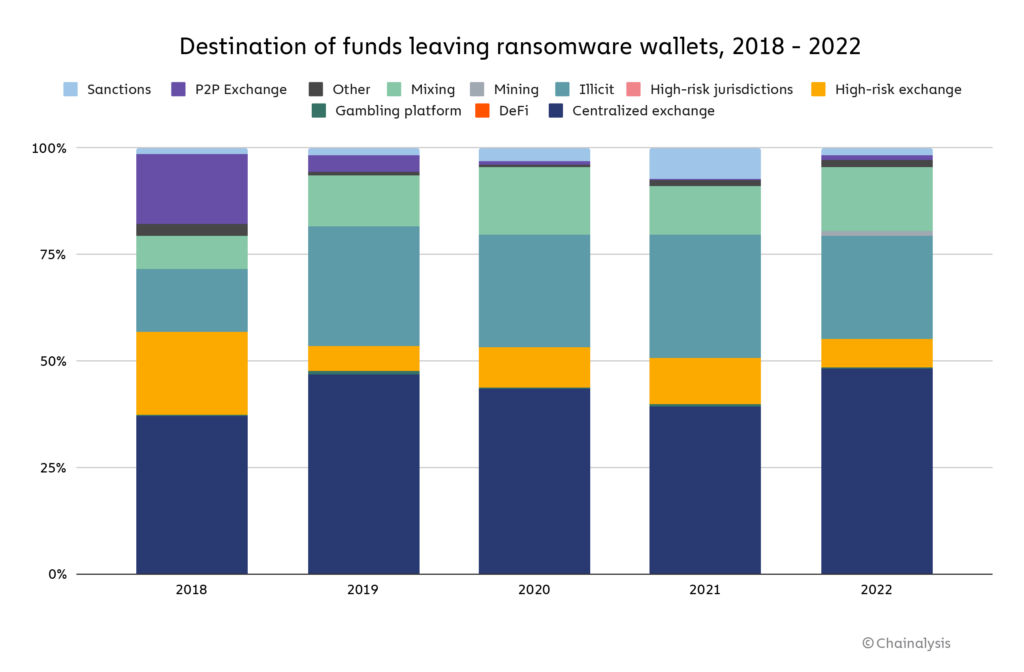
Funds acquired by ransomware assaults are laundered by a number of avenues. The vast majority of funds are nonetheless despatched to fashionable centralized exchanges. Nevertheless, P2P exchanges, a well-liked answer for ransomware attackers in 2018, now make up a tiny proportion of the general quantity.
After centralized exchanges, a persistent methodology of laundering funds is utilizing darknet markets designated as ‘illicit’ within the Chainalysis chart beneath. Lastly, mixing providers make up the following most good portion, permitting attackers to ‘wash’ crypto with little recourse from world authorities.
On-chain knowledge forensics
Chainalysis used on-chain knowledge to establish “affiliate” markets for ransomware software program whereby third events obtain a “small, mounted minimize of the proceeds” in a ransomware-as-a-service mannequin.
“We will consider it because the gig financial system, however for ransomware. A rideshare driver could have his Uber, Lyft, and Oja apps open without delay, creating the phantasm of three separate drivers on the highway — however in actuality, it’s all the identical automotive.”
On-chain knowledge has allowed corporations like Chainalysis to hint unhealthy actors throughout the blockchain and presumably establish the following assault vector. For instance, Conti, a prevalent ransomware pressure, was disbanded in Could 2022. But, on-chain knowledge has revealed that wallets related to Conti at the moment are shifting onto different strains corresponding to Royal, Quantum, and Ragnar.
Ransomware attackers “re-used wallets for a number of assaults launched nominally underneath different strains,” making tracing exercise comparatively elementary.
Decline in ransomware funds
The variety of profitable ransomware assaults fell as a result of elevated understanding of the panorama, improved safety measures, and higher on-chain forensic capabilities. Consequently, victims are refusing to pay attackers, as many are linked to OFAC-sanctioned events.
In 2019 simply 24% of victims refused to pay, whereas, in 2022, the share elevated to 59%. Paying a ransomware bounty to a celebration on the OFAC sanctions checklist might now be “legally riskier.” Allan Lisk, an intelligence analyst at Recorded Future, informed Chainalysis;
“With the specter of sanctions looming, there’s the added menace of authorized penalties for paying [ransomware attackers.]”
The implications of not paying ransomware calls for can typically devastate the victims, who typically lose entry to important knowledge. Nevertheless, because the illicit business turns into much less financially viable, the hope is that the variety of assaults additionally falls, thus lowering the variety of victims.
Regardless, the position of cryptocurrency in ransomware assaults is obvious. It’s a methodology to steal a whole lot of thousands and thousands of {dollars} price of crypto annually. Nevertheless, that isn’t to say that there isn’t extra misplaced to conventional monetary property, a lot of which aren’t traceable by a blockchain.



